端口扫描如何工作?
如下图所示,JSFiddle在端口21、22、23、25、53、80、443、445、5900和8080上扫描192.168.88.1。
var ports = [21, 22, 23, 25, 53, 80, 443, 445, 5900, 8080];
var target = "192.168.88.1";
address_div = document.createElement('div');
address_div.id = target;
address_div.innerHTML = target;
document.getElementById("hosts").appendChild(address_div);
var scan_array = [];
for (i = 0; i < ports.length; i++) {
probe_address = "turn:" + target + ":" + ports[i] + "?transport=tcp";
scan_array.push({
urls: probe_address,
credential: "lobster",
username: "albino"
});
port_div = document.createElement('div');
port_div.id = ports[i]
port_div.innerHTML = " -> Port " + ports[i] + " - ?"
document.getElementById(target).appendChild(port_div);
}
var port_scan = new RTCPeerConnection({
iceServers: scan_array,
iceCandidatePoolSize: 0
});
port_scan.createDataChannel('', {
reliable: false
});
port_scan.onicecandidateerror = function(e) {
if (e.url == null) {
return;
}
url_split = e.url.split(":");
port_split = url_split[2].split("?");
if (e.hostCandidate != "0.0.0.x:0") {
document.getElementById(port_split[0]).innerHTML = " -> Port " + port_split[0] + " - <b><i>Open</i><b>"
} else {
document.getElementById(port_split[0]).innerHTML = " -> Port " + port_split[0] + " - Closed"
}
}
setTimeout(function() {
if (port_scan.iceGatheringState === "gathering") {
port_scan.close();
}
}, 60000);
port_scan.onicegatheringstatechange = function(e) {
if (port_scan.iceGatheringState == "complete") {
port_scan.close();
}
}
port_scan.createOffer(function(offerDesc) {
port_scan.setLocalDescription(offerDesc);
},
function(e) {
console.log("Create offer failed callback.");
});
<html>
<body>
<div id="hosts">
</div>
</body>
</html>
192.168.88.1 -> Port 21 - ? -> Port 22 - ? -> Port 23 - ? -> Port 25 - ? -> Port 53 - ? -> Port 80 - ? -> Port 443 - ? -> Port 445 - ? -> Port 5900 - ? -> Port 8080 - ?
在我的本地网络上运行后的结果如下:
这是一个研究设备,不用担心。
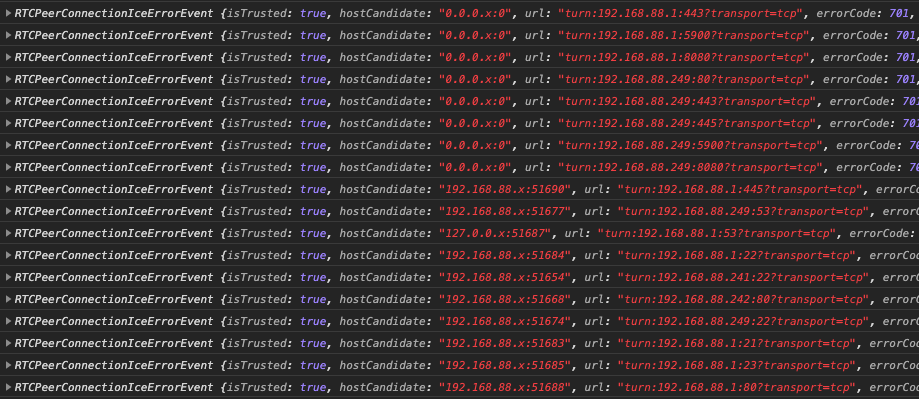
根据Chrome生成icecandidateerror事件的方式,该脚本将端口归类为“打开”或“关闭”。每个icecandidateerror都有一个hostCandidate变量。任何完成TCP三向握手的ICE服务器都将在hostCandidate中列出本地IP和端口(例如192.168.88.x:51688)。无法访问的ICE服务器会生成“ 0.0.0.x:0”形式的hostCandidates。因此确定端口是否打开变得很简单。
扫描我本地192.168.88.0/24上的活动主机而生成的控制台日志
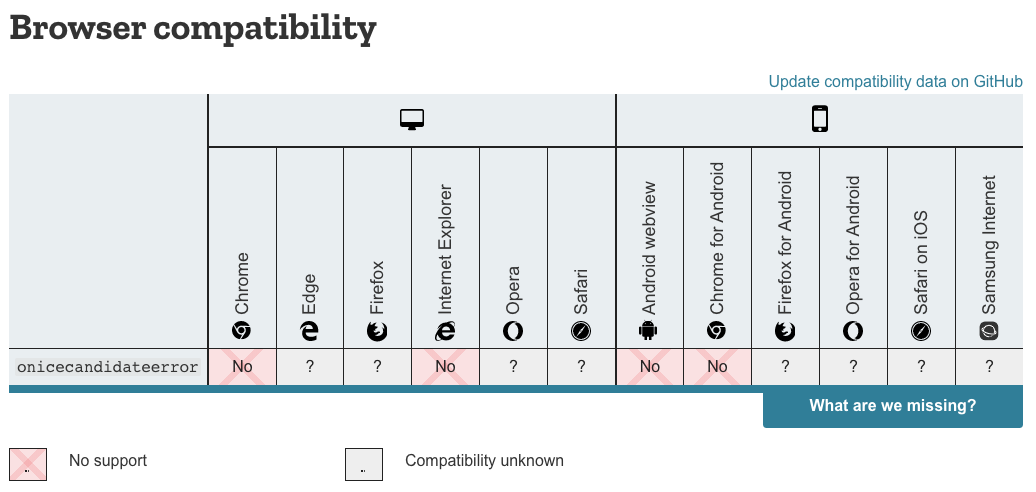
仅适用于Chrome吗?
我无法在其他任何浏览器中重新创建此操作。可能是因为其他浏览器未实现onicecandidateerror。也因为MDN表示“不支持”,所以Chrome刚开始使用此工具。
MDN指出,此页面的最新更新时间为2019年3月18日。
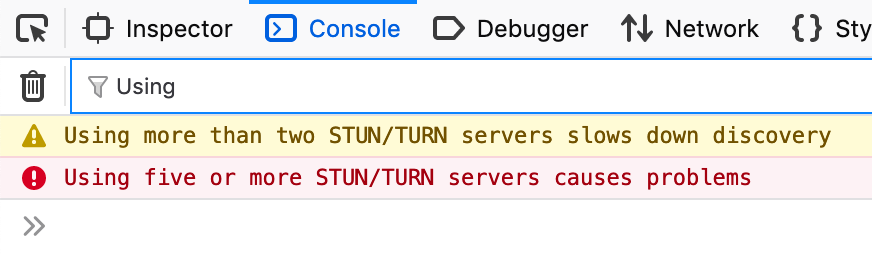
其他浏览器对我使用RTCPeerConnection似乎并不感冒。虽然Chrome乐于接受255种不同的ICE服务器,但如果您提供两个以上的Firefox,Firefox就很开心了。
概念代码的证明
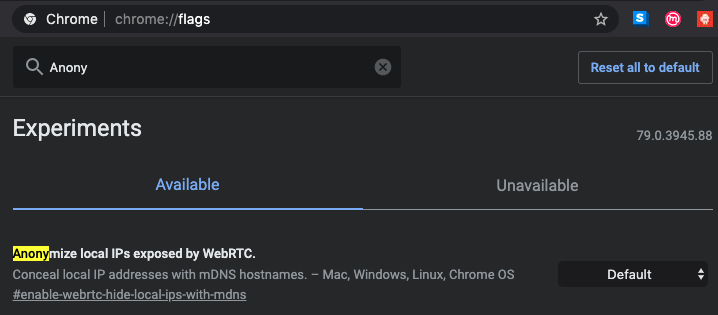
Chrome最近的进展是:已采取措施借助WebRTC修复本地地址的泄漏问题。在启用“实验性”功能和“匿名化WebRTC公开的本地IP”标志时,Chrome会尝试使用mDNS .local主机名代替本地IP。
我赞同这样的变化。因为即使是我这种很少进行网络研究的人,也已经在公开场合中利用WebRTC IP泄漏进行了操作。那么对于网络专家来说应该更有用。
无论如何,概念验证已将上述问题考虑在内。如果无法获得IPv4地址,它将在192.168.[0–255].1上的某个位置搜索有效IP。如果您在其他专用子网中,概念验证会继续尝试扫描127.0.0.1。
这是漏洞吗?
最初我觉得这是一个漏洞。(假设)攻击者绕过了Chrome的受限端口列表,并能够映射受害者的LAN——(我认为)即CWE-184、CWE-284和CWE-200的组合。但是Google似乎将此视为“指纹识别”问题。因为他们在“网络配置指纹”这一项中特别注明:
“使用主动探测时,本地主机上打开的端口列表指示系统上其他已安装的软件和防火墙设置。不守规矩的参与者也可能会试探访客本地网络中的系统和服务;直接在浏览器中执行此操作将避开特定的防火墙,即通常会过滤掉不需要传入流量的那些防火墙。”
根据Google的说法,指纹识别是一个隐私问题,而不是一个漏洞。
“尽管我们不将指纹问题视为安全漏洞,但我们将其视为隐私漏洞。”
有解决办法吗?
是。有各种各样声称完全禁用WebRTC的Chrome扩展程序。您也可以选择使用其他浏览器。
文章作者:Jacob Baines